Templat:Kotak info kopernisium
Tampilan
(Dialihkan dari Templat:Infobox kopernisium)
112Cn Kopernisium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
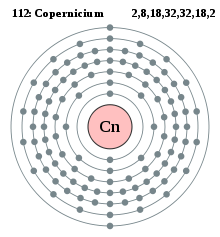 Konfigurasi elektron kopernisium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan | /kopêrnisium/ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kopernisium dalam tabel periodik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 112 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | logam transisi, pernah dipertimbangkan sebagai logam miskin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor massa | [285] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 (diprediksi)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 2 (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | cair (diprediksi) [2][3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 283 ± 11 K (10 ± 11 °C, 50 ± 20 °F) (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 340 ± 10 K (67 ± 10 °C, 153 ± 18 °F)[3] (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 14,0 g/cm3 (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik tripel | 283 K, 25 kPa (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | 0, (+1), +2, (+4), (+6) (tanda kurung: prediksi)[1][4][5][6] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 1155 kJ/mol ke-2: 2170 kJ/mol ke-3: 3160 kJ/mol (artikel) (semuanya merupakan perkiraan)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | perhitungan: 147 pm[1][5] (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 122 pm (diprediksi)[7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | sintetis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | susunan padat heksagon (hcp) (diprediksi)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 54084-26-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari N. Copernicus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan | Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (1996) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop kopernisium yang utama | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Navigasi unsur
Referensi
- ^ a b c d Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". Dalam Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (edisi ke-3). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ Soverna S 2004, 'Indication for a gaseous element 112,' in U Grundinger (ed.), GSI Scientific Report 2003, GSI Report 2004-1, p. 187, ISSN 0174-0814
- ^ a b c d e f Mewes, J.-M.; Smits, O. R.; Kresse, G.; Schwerdtfeger, P. (2019). "Copernicium is a Relativistic Noble Liquid". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. doi:10.1002/anie.201906966.
- ^ Gäggeler, Heinz W.; Türler, Andreas (2013). "Gas Phase Chemistry of Superheavy Elements". The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements. Springer Science+Business Media. hlm. 415–483. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-37466-1_8. ISBN 978-3-642-37465-4. Diakses tanggal 16 Juli 2022.
- ^ a b Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. Structure and Bonding. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. ISBN 978-3-540-07109-9. Diakses tanggal 16 Juli 2022.
- ^ Hu, Shu-Xian; Zou, Wenli (23 September 2021). "Stable copernicium hexafluoride (CnF6) with an oxidation state of VI+". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2022 (24): 321–325. doi:10.1039/D1CP04360A.
- ^ Chemical Data. Copernicium - Cn, Royal Chemical Society
- ^ Utyonkov, V. K.; Brewer, N. T.; Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; et al. (30 Januari 2018). "Neutron-deficient superheavy nuclei obtained in the 240Pu+48Ca reaction". Physical Review C. 97 (14320): 1–10. Bibcode:2018PhRvC..97a4320U. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.014320.
- ^ Chart of Nuclides. Brookhaven National Laboratory
- ^ Såmark-Roth, A.; Cox, D. M.; Rudolph, D.; et al. (2021). "Spectroscopy along Flerovium Decay Chains: Discovery of 280Ds and an Excited State in 282Cn". Physical Review Letters. 126: 032503. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.032503.
Penggunaan
[sunting sumber]55Cs Sesium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Sampel sesium di dalam ampul kaca | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Garis spektrum sesium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penampilan | emas pucat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sesium dalam tabel periodik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 1 (logam alkali) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | logam alkali | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Berat atom standar (Ar) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Xe] 6s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | padat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 301,7 K (28,5 °C, 83,3 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 944 K (671 °C, 1240 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 1,93 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| saat cair, pada t.l. | 1,843 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik kritis | 1938 K, 9,4 MPa[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor peleburan | 2,09 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor penguapan | 63,9 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kapasitas kalor molar | 32,210 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tekanan uap
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | −1, +1[3] (oksida basa kuat) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektronegativitas | Skala Pauling: 0,79 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 375,7 kJ/mol ke-2: 2234,3 kJ/mol ke-3: 3400 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | empiris: 265 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 244±11 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari van der Waals | 343 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | kubus berpusat badan (bcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ekspansi kalor | 97 µm/(m·K) (suhu 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konduktivitas termal | 35,9 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resistivitas listrik | 205 nΩ·m (suhu 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arah magnet | paramagnetik[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus Young | 1,7 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus curah | 1,6 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Skala Mohs | 0,2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Skala Brinell | 0,14 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 7440-46-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari bahasa Latin caesius, 'abu-abu kebiruan', karena warna spektrumnya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan | R. Bunsen dan G. Kirchhoff (1860) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isolasi pertama | C. Setterberg (1882) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop sesium yang utama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Referensi
- ^ (Indonesia) "Sesium". KBBI Daring. Diakses tanggal 17 Juli 2022.
- ^ (Inggris) Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (edisi ke-92). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. hlm. 4.121. ISBN 1439855110.
- ^ (Inggris) Dye, J. L. (1979). "Compounds of Alkali Metal Anions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 18 (8): 587–598. doi:10.1002/anie.197905871.
- ^ (Inggris) "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (edisi ke-87). CRC press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3. Diakses tanggal 29 Juli 2022.
- ^ (Inggris) "NIST Radionuclide Half-Life Measurements". NIST. Diakses tanggal 29 Juli 2022.



