Templat:Kotak info oganeson
Tampilan
(Dialihkan dari Templat:Infobox oganeson)
118Og Oganeson | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
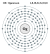
 Konfigurasi elektron oganeson | |||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | |||||||||||||
| Pengucapan | /oganèson/ | ||||||||||||
| Oganeson dalam tabel periodik | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 118 | ||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 18 | ||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 7 | ||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-p | ||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | sebelumnya diperkirakan sebagai gas mulia, tetapi sekarang diprediksi berbentuk padatan reaktif yang tampak seperti logam, dan berupa semikonduktor (mungkin metaloid) atau logam miskin.[1][2] | ||||||||||||
| Nomor massa | [294] | ||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Rn] 5f14 6d10 7s2 7p6 (diprediksi)[3][4] | ||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 8 (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | |||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | padat (diprediksi)[5] | ||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 325 ± 15 K (52 ± 15 °C, 125 ± 27 °F) (diprediksi)[5] | ||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 450 ± 10 K (177 ± 10 °C, 350 ± 18 °F) (diprediksi)[5] | ||||||||||||
| Kepadatan saat cair, pada t.l. | 6,6–7,4 g/cm3 (diprediksi)[5] | ||||||||||||
| Titik kritis | 439 K, 6,8 MPa (diekstrapolasi)[6] | ||||||||||||
| Kalor peleburan | 23,5 kJ/mol (diekstrapolasi)[6] | ||||||||||||
| Kalor penguapan | 19,4 kJ/mol (diekstrapolasi)[6] | ||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | |||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | (−1),[4] (0), (+1),[7] (+2),[8] (+4),[8] (+6)[4] (diprediksi) | ||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 860,1 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[9] ke-2: 1560 kJ/mol (diprediksi)[10] | ||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | empiris: 152 pm (diprediksi)[11] | ||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 157 pm (diprediksi)[12] | ||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | |||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | sintetis | ||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | kubus berpusat muka (fcc) (diekstrapolasi)[13] | ||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 54144-19-3 | ||||||||||||
| Sejarah | |||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari Yuri Oganessian | ||||||||||||
| Prediksi | Hans J. Thomsen (1895) | ||||||||||||
| Penemuan | Joint Institute for Nuclear Research dan Laboratorium Nasional Lawrence Livermore (2002) | ||||||||||||
| Isotop oganeson yang utama | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Navigasi unsur
- Referensi placeholder.[16]
Referensi
- ^ Mewes, Jan-Michael; Smits, Odile Rosette; Jerabek, Paul; Schwerdtfeger, Peter (25 Juli 2019). "Oganesson is a Semiconductor: On the Relativistic Band‐Gap Narrowing in the Heaviest Noble‐Gas Solids". Angewandte Chemie. doi:10.1002/anie.201908327. Diakses tanggal 11 Agustus 2022.
- ^ Gong, Sheng; Wu, Wei; Wang, Fancy Qian; Liu, Jie; Zhao, Yu; Shen, Yiheng; Wang, Shuo; Sun, Qiang; Wang, Qian (8 Februari 2019). "Classifying superheavy elements by machine learning". Physical Review A. 99: 022110–1–7. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.99.022110.
- ^ Nash, Clinton S. (2005). "Atomic and Molecular Properties of Elements 112, 114, and 118". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 109 (15): 3493–3500. doi:10.1021/jp050736o. PMID 16833687.
- ^ a b c Hoffman, Darleane C.; Lee, Diana M.; Pershina, Valeria (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". Dalam Morss; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements (edisi ke-3). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5.
- ^ a b c d Smits, Odile; Mewes, Jan-Michael; Jerabek, Paul; Schwerdtfeger, Peter (2020). "Oganesson: A Noble Gas Element That Is Neither Noble Nor a Gas". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 (52): 23636–23640. doi:10.1002/anie.202011976. PMC 7814676
 . PMID 32959952.
. PMID 32959952.
- ^ a b c Eichler, R.; Eichler, B., Thermochemical Properties of the Elements Rn, 112, 114, and 118 (PDF), Paul Scherrer Institut, diakses tanggal 11 Agustus 2022
- ^ Han, Young-Kyu; Bae, Cheolbeom; Son, Sang-Kil; Lee, Yoon Sup (2000). "Spin–orbit effects on the transactinide p-block element monohydrides MH (M=element 113–118)". Journal of Chemical Physics. 112 (6): 2684. Bibcode:2000JChPh.112.2684H. doi:10.1063/1.480842.
- ^ a b Kaldor, Uzi; Wilson, Stephen (2003). Theoretical Chemistry and Physics of Heavy and Superheavy Elements. Springer. hlm. 105. ISBN 978-1402013713. Diakses tanggal 6 Agustus 2022.
- ^ Pershina, Valeria (30 November 2013). "Theoretical Chemistry of the Heaviest Elements". Dalam Schädel, Matthias; Shaughnessy, Dawn. The Chemistry of Superheavy Elements (edisi ke-2). Springer Science & Business Media. hlm. 154. ISBN 9783642374661.
- ^ Fricke, Burkhard (1975). "Superheavy elements: a prediction of their chemical and physical properties". Recent Impact of Physics on Inorganic Chemistry. 21: 89–144. doi:10.1007/BFb0116498. Diakses tanggal 11 Agustus 2022.
- ^ Oganesson, American Elements
- ^ Oganesson - Element information, properties and uses, Royal Chemical Society
- ^ Grosse, A. V. (1965). "Some physical and chemical properties of element 118 (Eka-Em) and element 86 (Em)". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. Elsevier Science Ltd. 27 (3): 509–19. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(65)80255-X.
- ^ Oganessian, Yu. Ts.; Utyonkov, V. K.; Lobanov, Yu. V.; Abdullin, F. Sh.; Polyakov, A. N.; Sagaidak, R. N.; Shirokovsky, I. V.; Tsyganov, Yu. S.; Voinov, A. A.; Gulbekian, G. G.; Bogomolov, S. L.; Gikal, B. N.; Mezentsev, A. N.; Iliev, S.; Subbotin, V. G.; Sukhov, A. M.; Subotic, K.; Zagrebaev, V. I.; Vostokin, G. K.; Itkis, M. G.; Moody, K. J.; Patin, J. B.; Shaughnessy, D. A.; Stoyer, M. A.; Stoyer, N. J.; Wilk, P. A.; Kenneally, J. M.; Landrum, J. H.; Wild, J. F.; Lougheed, R. W. (2006-10-09). "Synthesis of the isotopes of elements 118 and 116 in the 249Cf and 245Cm+48Ca fusion reactions". Physical Review C. 74 (4): 044602. Bibcode:2006PhRvC..74d4602O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.74.044602. Diakses tanggal 11 Agustus 2022.
- ^ Oganessian, Yuri Ts.; Rykaczewski, Krzysztof P. (August 2015). "A beachhead on the island of stability". Physics Today. 68 (8): 32–38. Bibcode:2015PhT....68h..32O. doi:10.1063/PT.3.2880. OSTI 1337838.
- ^ (Placeholder untuk referensi Nama resmi yang diusulkan.
<ref name="IUPAC-June2016">...</ref>harus didefinisikan dalam teks artikel.)
Penggunaan
[sunting sumber]55Cs Sesium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Sampel sesium di dalam ampul kaca | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Garis spektrum sesium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat umum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pengucapan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penampilan | emas pucat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sesium dalam tabel periodik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor atom (Z) | 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Golongan | golongan 1 (logam alkali) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Periode | periode 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blok | blok-s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kategori unsur | logam alkali | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Berat atom standar (Ar) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konfigurasi elektron | [Xe] 6s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektron per kelopak | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat fisik | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fase pada STS (0 °C dan 101,325 kPa) | padat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik lebur | 301,7 K (28,5 °C, 83,3 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik didih | 944 K (671 °C, 1240 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kepadatan mendekati s.k. | 1,93 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| saat cair, pada t.l. | 1,843 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Titik kritis | 1938 K, 9,4 MPa[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor peleburan | 2,09 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalor penguapan | 63,9 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kapasitas kalor molar | 32,210 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tekanan uap
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sifat atom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilangan oksidasi | −1, +1[3] (oksida basa kuat) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elektronegativitas | Skala Pauling: 0,79 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energi ionisasi | ke-1: 375,7 kJ/mol ke-2: 2234,3 kJ/mol ke-3: 3400 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari atom | empiris: 265 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari kovalen | 244±11 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jari-jari van der Waals | 343 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lain-lain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelimpahan alami | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Struktur kristal | kubus berpusat badan (bcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ekspansi kalor | 97 µm/(m·K) (suhu 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Konduktivitas termal | 35,9 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resistivitas listrik | 205 nΩ·m (suhu 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arah magnet | paramagnetik[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus Young | 1,7 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modulus curah | 1,6 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Skala Mohs | 0,2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Skala Brinell | 0,14 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nomor CAS | 7440-46-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sejarah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penamaan | dari bahasa Latin caesius, 'abu-abu kebiruan', karena warna spektrumnya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Penemuan | R. Bunsen dan G. Kirchhoff (1860) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isolasi pertama | C. Setterberg (1882) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotop sesium yang utama | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Referensi
- ^ (Indonesia) "Sesium". KBBI Daring. Diakses tanggal 17 Juli 2022.
- ^ (Inggris) Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (edisi ke-92). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. hlm. 4.121. ISBN 1439855110.
- ^ (Inggris) Dye, J. L. (1979). "Compounds of Alkali Metal Anions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 18 (8): 587–598. doi:10.1002/anie.197905871.
- ^ (Inggris) "Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds". Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (PDF) (edisi ke-87). CRC press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3. Diakses tanggal 29 Juli 2022.
- ^ (Inggris) "NIST Radionuclide Half-Life Measurements". NIST. Diakses tanggal 29 Juli 2022.