Hipotesis dunia PAH
Tampilan
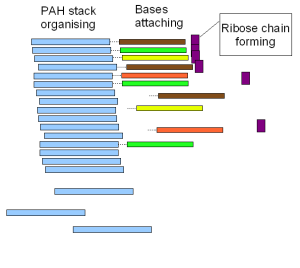
Hipotesis dunia PAH adalah sebuah hipotesis spekulatif yang menyatakan bahwa hidrokarbon aromatik polisiklik (PAH), senyawa organik yang jumlahnya melimpah di alam semesta,[1][2][3] termasuk di dalam komet,[4] dan diperkirakan juga melimpah di sup purba Bumi, memainkan peran utama dalam asal usul kehidupan sebagai perantara bagi sintesis molekul RNA, yang mengarah pada dunia RNA. Namun, sampai sekarang hipotesis ini masih belum diuji.[5]
Referensi
[sunting | sunting sumber]- ^ Carey, Bjorn (18 Oktober 2005). "Life's Building Blocks 'Abundant in Space'". Space.com. Diakses tanggal 3 Maret 2014.
- ^ Hudgins, Douglas M.; Bauschlicher,Jr, Charles W.; Allamandola, L. J. (10 Oktober 2005). "Variations in the Peak Position of the 6.2 μm Interstellar Emission Feature: A Tracer of N in the Interstellar Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Population". Astrophysical Journal. 632 (1): 316–332. Bibcode:2005ApJ...632..316H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.218.8786
 . doi:10.1086/432495.
. doi:10.1086/432495.
- ^ Allamandola, Louis et al. (13 April 2011). "Cosmic Distribution of Chemical Complexity". NASA. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 27 Februari 2014. Diakses tanggal 3 Maret 2014.
- ^ Clavin, Whitney (10 Februari 2015). "Why Comets Are Like Deep Fried Ice Cream". NASA. Diakses tanggal 10 Februari 2015.
- ^ Platts, Simon Nicholas, "The PAH World - Discotic polynuclear aromatic compounds as a mesophase scaffolding at the origin of life"
Pranala luar
[sunting | sunting sumber]

